Clinical Research
(CR-064) Evaluation of lymphatic vessel insufficiency in lower limb lymphedema stages 0 and I.
Friday, April 28, 2023
7:15 PM - 8:30 PM East Coast USA Time
Natalia Krzesniak, PhD
Introduction: Introduction. Spontaneous, autoregulated lymphangion contraction is the main force propelling lymph along the lymphatic. Some events, such as inflammation and trauma, may destroy lymphatic valves and endothelial and muscle cells. Consequently, lymphatic vessels became insufficient in lymph transport. On ICG lymphography, we can observe and analyze the lymphatic contraction (pulse). Usually, the first changes are slower lymph flow and lymphatics dilatation. Early diagnosis of lymphatic vessel insufficiency and prophylaxis implementation can stop further destructive changes leading to advanced edema with tissue changes.
Aim. To evaluate foot and calf lymphatics collector contraction capacity and lymph flow in the early stages of lymphedema.
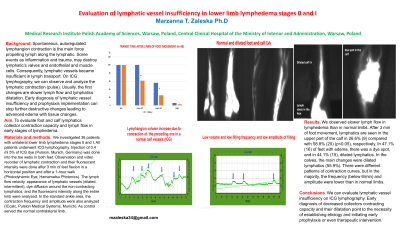
Methods: . We investigated 36 patients with unilateral lower limb lymphedema stage I. All patients underwent ICG lymphography. Injection of 0.4 ml 5% of ICG dye (Pulsion, Munich, Germany) was injected into both feet' toe webs. Observation and video recorder of lymphatic contraction and their fluorescent intensity were done after 3 min of feet flexion in a horizontal position and after a 1-hour walk (Photodynamic Eye; Hamamatsu Photonics). The lymph flow velocity, appearance of lymphatic vessels (dilated, intermittent), dye diffusion around the non-contracting lymphatics, and the fluorescent intensity along the entire limb were analyzed. In the standard ankle area, the contraction frequency and amplitude were also analyzed (ICcalc, Pulsion Medical Systems, Munich) as control served the normal contralateral limb.
Results: We observed slower lymph flow in lymphedema than in normal limbs. After 3 min of foot movement, lymphatics are seen in the upper part of the calf in 26.6% (9) compared with 58.8% (20) (p< 0.05), respectively. In 47.1% (16) of feet with edema, there was a dye spot, and in 44.1% (15), dilated lymphatics. In the calves, the main changes were dilated lymphatics (55.9%). There were different patterns of contraction curves (the examples will be shown), but in the majority, the frequency (below 6/min) and amplitude were lower than in normal limbs.
Discussion: We can evaluate lymphatic vessel insufficiency on ICG lymphography. Early diagnosis of decreased collectors contracting capacity and their dilatation point to the necessity of establishing etiology and initiating early prophylaxis or even therapeutic intervention.
Aim. To evaluate foot and calf lymphatics collector contraction capacity and lymph flow in the early stages of lymphedema.
Methods: . We investigated 36 patients with unilateral lower limb lymphedema stage I. All patients underwent ICG lymphography. Injection of 0.4 ml 5% of ICG dye (Pulsion, Munich, Germany) was injected into both feet' toe webs. Observation and video recorder of lymphatic contraction and their fluorescent intensity were done after 3 min of feet flexion in a horizontal position and after a 1-hour walk (Photodynamic Eye; Hamamatsu Photonics). The lymph flow velocity, appearance of lymphatic vessels (dilated, intermittent), dye diffusion around the non-contracting lymphatics, and the fluorescent intensity along the entire limb were analyzed. In the standard ankle area, the contraction frequency and amplitude were also analyzed (ICcalc, Pulsion Medical Systems, Munich) as control served the normal contralateral limb.
Results: We observed slower lymph flow in lymphedema than in normal limbs. After 3 min of foot movement, lymphatics are seen in the upper part of the calf in 26.6% (9) compared with 58.8% (20) (p< 0.05), respectively. In 47.1% (16) of feet with edema, there was a dye spot, and in 44.1% (15), dilated lymphatics. In the calves, the main changes were dilated lymphatics (55.9%). There were different patterns of contraction curves (the examples will be shown), but in the majority, the frequency (below 6/min) and amplitude were lower than in normal limbs.
Discussion: We can evaluate lymphatic vessel insufficiency on ICG lymphography. Early diagnosis of decreased collectors contracting capacity and their dilatation point to the necessity of establishing etiology and initiating early prophylaxis or even therapeutic intervention.

.png)